 Enterprise Value (EV) or Firm Value is an economic measure that indicates the total value of a company. It measures how much an acquirer needs to pay to buy a company. It’s one of the fundamental metrics used in business valuation and portfolio analysis.
Enterprise Value (EV) or Firm Value is an economic measure that indicates the total value of a company. It measures how much an acquirer needs to pay to buy a company. It’s one of the fundamental metrics used in business valuation and portfolio analysis.
Enterprise Value is considered to be more comprehensive and accurate than market capitalization while valuing a business. It takes into account not only the equity value of the company, but also its debt, cash and minority interest. Market capitalization, on the other hand, includes only common equity (leaving out important factors like company’s debt and its cash reserves.)
Calculating Enterprise Value of a firm
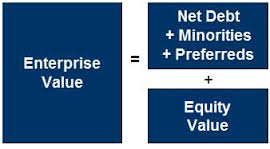
Simply put, Enterprise Value is the sum of market capitalization and net debt of a company. Mathematically,
Enterprise Value = Market Capitalization + Debt + Preferred Stock + Minority Interest + Pension Liabilities and other debt-deemed provisions – Cash and cash equivalents – “Extra Assets” – Investments
Where,
- Market Capitalization is the price of each share x number of common shares outstanding. So, if a company has 100 common shares outstanding with each share selling at $10, its market capitalization will be $1,000.
